
Thus, the columns of the periodic table represent the potential shared state of these elements' outer electron shells that is responsible for their similar chemical characteristics.
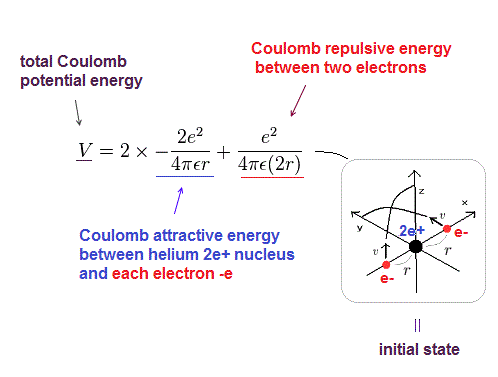
When an atom gains an electron to become a negatively-charged ion this is indicated by a minus sign after the element symbol for example, \(F^-\). The ring structure of a simple atom showing protons and neutrons at the center with electrons Figure 1: Model of a Helium atom illustrating protons and. We'll use a Bohr diagram to visually represent. That means it has 2 number protons, 2 number of electrons and 2 number of neutrons. Group 17 elements, including fluorine and chlorine, have seven electrons in their outermost shells they tend to fill this shell by gaining an electron from other atoms, making them negatively-charged ions. In this video we'll look at the atomic structure and Bohr model for the Helium atom (He). As we know that the atomic number of helium atom is 2.
Helium bohr model plus#
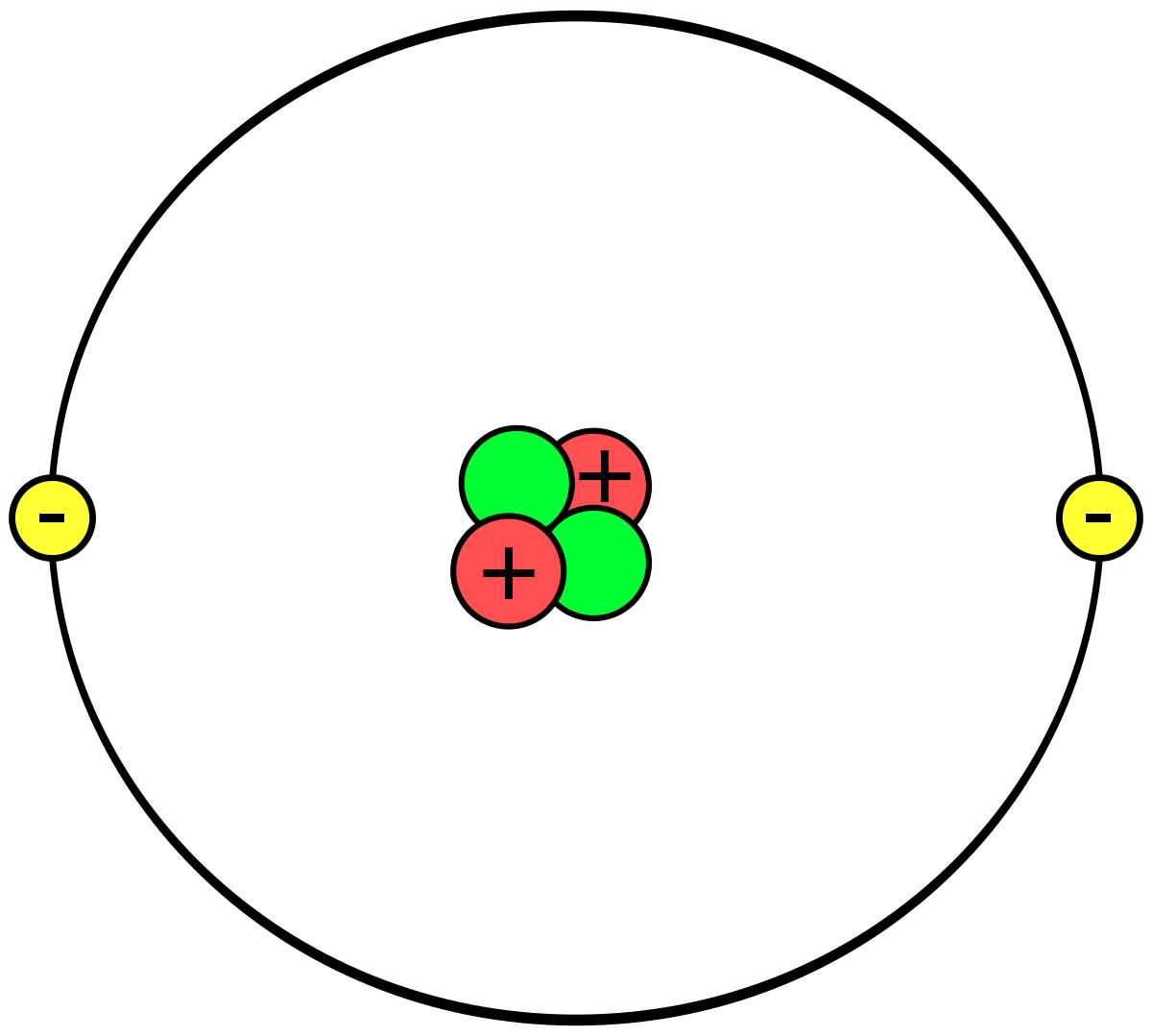
When an atom loses an electron to become a positively-charged ion, this is indicated by a plus sign after the element symbol for example, Na +. As a result of losing a negatively-charged electron, they become positively-charged ions. This means that they can achieve a stable configuration and a filled outer shell by donating or losing an electron. In comparison, the group 1 elements, including hydrogen (H), lithium (Li), and sodium (Na), all have one electron in their outermost shells. Unlike planets orbiting the Sun, electrons cannot be at any arbitrary distance from the nucleus they can exist only in certain specific locations called allowed orbits. Their non-reactivity has resulted in their being named the inert gases (or noble gases). As shown in, the group 18 atoms helium (He), neon (Ne), and argon (Ar) all have filled outer electron shells, making it unnecessary for them to gain or lose electrons to attain stability they are highly stable as single atoms. A type Ia supernova shows the presence of helium-rich circumstellar material, as demonstrated by its spectral features, infrared emission and a radio counterpart, that probably originates from a. The periodic table is arranged in columns and rows based on the number of electrons and where these electrons are located, providing a tool to understand how electrons are distributed in the outer shell of an atom.
Helium bohr model full#
Elements in other groups have partially-filled valence shells and gain or lose electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration.Īn atom may gain or lose electrons to achieve a full valence shell, the most stable electron configuration. A full valence shell is the most stable electron configuration. The Bohr model: Journey to find structure of atoms. (b) The energy of the orbit becomes increasingly less negative with increasing n. 2 The Bohr Model of the Hydrogen Atom (a) The distance of the orbit from the nucleus increases with increasing n. Group 18 elements (helium, neon, and argon are shown) have a full outer, or valence, shell. Niels Bohr's model of the atom provided a wonderfully accurate explanation of the spectrum of hydrogen, but when it was applied to the spectrum of helium it failed.Werner Heisenberg developed a modification of Bohr's analysis but it involved half-integral values for the quantum numbers. In this state the radius of the orbit is also infinite. Rutherford’s earlier model of the atom had also assumed that electrons moved in circular orbits around the nucleus and that the atom was held together by the electrostatic attraction between the positively charged nucleus and the negatively charged electron.\):īohr diagrams indicate how many electrons fill each principal shell. Bohr’s model required only one assumption: The electron moves around the nucleus in circular orbits that can have only certain allowed radii. In 1913, a Danish physicist, Niels Bohr (1885–1962 Nobel Prize in Physics, 1922), proposed a theoretical model for the hydrogen atom that explained its emission spectrum. Goals: Students will be able to build Bohrs models of Hydrogen, Helium.
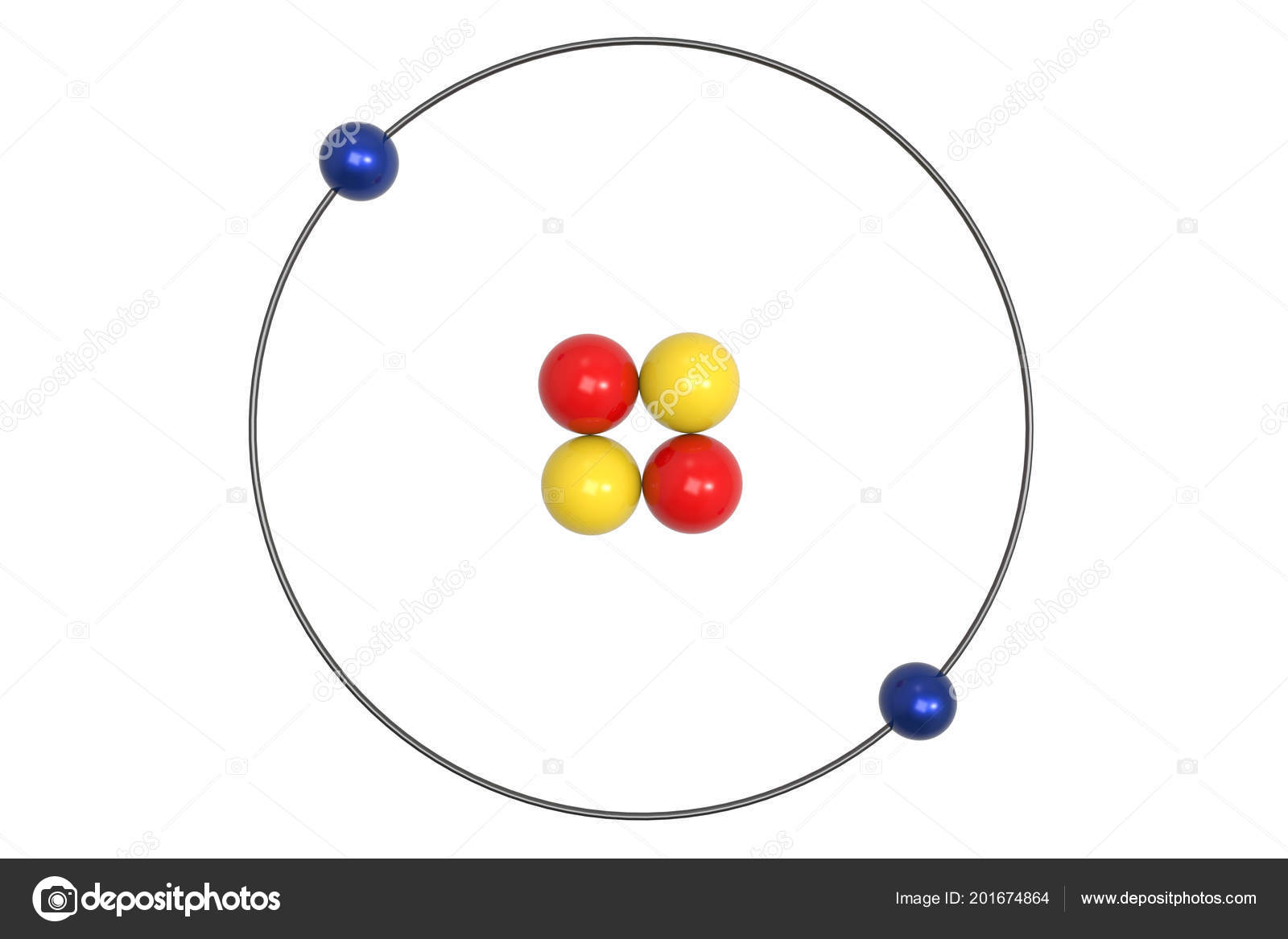
Where \(n_1\) and \(n_2\) are positive integers, \(n_2 > n_1\), and \( \Re \) the Rydberg constant, has a value of 1.09737 × 10 7 m −1. Prerequisite knowledge/skills: Students were introduced to Bohrs model of an.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
